Code
library(tidyverse)
library(googlesheets4)
library(readxl)
knitr::opts_chunk$set(echo = TRUE, warning=FALSE, message=FALSE)Keith Martin
March 17, 2023
In this challenge, I decided to use the excel version of the Organice Poultry Data. Before I could read into the data, I needed to include libraries that allowed me to read in excel files.
After reading in the data, I noticed that there we’re three different tabs within the excel file. I decided to use only the data tab as this was the first excel file I have read into R.
[1] "Data" "Organic egg prices, 2004-13"
[3] "Organic poultry prices, 2004-13"I decided to re-name the names of the columns so they we’re more easily identified. This will become helpful later when I pivot the data longer. Additionally, there is a row that needed to be removed from the data that split the egg prices and the chicken prices. By re-naming the cells it is easier to analyze the data.
raw_poulty<-read_excel("_data/organiceggpoultry.xls",
sheet = "Data",
range =cell_limits(c(6,2),c(NA,12)),
col_names = c("date", "XL_Dozen", "XL_1/2_Doz.", "L_Dozen", "L_1/2_Doz", "Remove", "Ckn_Whole", "Ckn_BS_Breast", "Ckn_Bone_Breast", "Ckn_Whole_legs", "Ckn_Thighs"),
)
raw_poulty %>%
select(-c(Remove))# A tibble: 120 × 10
date XL_Do…¹ XL_1/…² L_Dozen L_1/2…³ Ckn_W…⁴ Ckn_B…⁵ Ckn_B…⁶ Ckn_W…⁷ Ckn_T…⁸
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 Jan … 230 132 230 126 198. 646. too few 194. too few
2 Febr… 230 134. 226. 128. 198. 642. too few 194. 203
3 March 230 137 225 131 209 642. too few 194. 203
4 April 234. 137 225 131 212 642. too few 194. 203
5 May 236 137 225 131 214. 642. too few 194. 203
6 June 241 137 231. 134. 216. 641 too few 202. 200.375
7 July 241 137 234. 134. 217 642. 390.5 204. 199.5
8 Augu… 241 137 234. 134. 217 642. 390.5 204. 199.5
9 Sept… 241 136. 234. 130. 217 642. 390.5 204. 199.5
10 Octo… 241 136. 234. 128. 217 642. 390.5 204. 199.5
# … with 110 more rows, and abbreviated variable names ¹XL_Dozen,
# ²`XL_1/2_Doz.`, ³`L_1/2_Doz`, ⁴Ckn_Whole, ⁵Ckn_BS_Breast, ⁶Ckn_Bone_Breast,
# ⁷Ckn_Whole_legs, ⁸Ckn_Thighs# A tibble: 22 × 2
date n
<chr> <int>
1 April 10
2 August 10
3 December 10
4 February 8
5 February /1 2
6 Jan 2004 1
7 Jan 2005 1
8 Jan 2006 1
9 Jan 2007 1
10 Jan 2008 1
# … with 12 more rows### remove that /1 from the February date
raw_poulty_clean <-raw_poulty %>%
mutate(date = str_remove(date, " /1"))
### Separate the month and the year, fill the years in for the rest of the months
raw_poulty_clean<-raw_poulty_clean %>%
separate(date, into=c("month", "year"), sep =" ")%>%
fill(year)
raw_poulty_clean # A tibble: 120 × 12
month year XL_Do…¹ XL_1/…² L_Dozen L_1/2…³ Remove Ckn_W…⁴ Ckn_B…⁵ Ckn_B…⁶
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Jan 2004 230 132 230 126 NA 198. 646. too few
2 February 2004 230 134. 226. 128. NA 198. 642. too few
3 March 2004 230 137 225 131 NA 209 642. too few
4 April 2004 234. 137 225 131 NA 212 642. too few
5 May 2004 236 137 225 131 NA 214. 642. too few
6 June 2004 241 137 231. 134. NA 216. 641 too few
7 July 2004 241 137 234. 134. NA 217 642. 390.5
8 August 2004 241 137 234. 134. NA 217 642. 390.5
9 Septemb… 2004 241 136. 234. 130. NA 217 642. 390.5
10 October 2004 241 136. 234. 128. NA 217 642. 390.5
# … with 110 more rows, 2 more variables: Ckn_Whole_legs <dbl>,
# Ckn_Thighs <chr>, and abbreviated variable names ¹XL_Dozen, ²`XL_1/2_Doz.`,
# ³`L_1/2_Doz`, ⁴Ckn_Whole, ⁵Ckn_BS_Breast, ⁶Ckn_Bone_BreastThis data did not include the year for each month entry. There was also a mistake in the data that needed to be removed.
Additionally, the Chicken Bone Breast and the Chicken Thighs data containted characters rather than numbers. First, I had to change those words to 0. Then, I had to change them to a numerical number, rather than just a character.
# A tibble: 120 × 12
month year XL_Do…¹ XL_1/…² L_Dozen L_1/2…³ Remove Ckn_W…⁴ Ckn_B…⁵ Ckn_B…⁶
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Jan 2004 230 132 230 126 NA 198. 646. 0
2 February 2004 230 134. 226. 128. NA 198. 642. 0
3 March 2004 230 137 225 131 NA 209 642. 0
4 April 2004 234. 137 225 131 NA 212 642. 0
5 May 2004 236 137 225 131 NA 214. 642. 0
6 June 2004 241 137 231. 134. NA 216. 641 0
7 July 2004 241 137 234. 134. NA 217 642. 390.5
8 August 2004 241 137 234. 134. NA 217 642. 390.5
9 Septemb… 2004 241 136. 234. 130. NA 217 642. 390.5
10 October 2004 241 136. 234. 128. NA 217 642. 390.5
# … with 110 more rows, 2 more variables: Ckn_Whole_legs <dbl>,
# Ckn_Thighs <chr>, and abbreviated variable names ¹XL_Dozen, ²`XL_1/2_Doz.`,
# ³`L_1/2_Doz`, ⁴Ckn_Whole, ⁵Ckn_BS_Breast, ⁶Ckn_Bone_Breast# A tibble: 120 × 12
month year XL_Do…¹ XL_1/…² L_Dozen L_1/2…³ Remove Ckn_W…⁴ Ckn_B…⁵ Ckn_B…⁶
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Jan 2004 230 132 230 126 NA 198. 646. 0
2 February 2004 230 134. 226. 128. NA 198. 642. 0
3 March 2004 230 137 225 131 NA 209 642. 0
4 April 2004 234. 137 225 131 NA 212 642. 0
5 May 2004 236 137 225 131 NA 214. 642. 0
6 June 2004 241 137 231. 134. NA 216. 641 0
7 July 2004 241 137 234. 134. NA 217 642. 390.
8 August 2004 241 137 234. 134. NA 217 642. 390.
9 Septemb… 2004 241 136. 234. 130. NA 217 642. 390.
10 October 2004 241 136. 234. 128. NA 217 642. 390.
# … with 110 more rows, 2 more variables: Ckn_Whole_legs <dbl>,
# Ckn_Thighs <dbl>, and abbreviated variable names ¹XL_Dozen, ²`XL_1/2_Doz.`,
# ³`L_1/2_Doz`, ⁴Ckn_Whole, ⁵Ckn_BS_Breast, ⁶Ckn_Bone_BreastThe original clean data had 12 columns and 120 rows.
I pivoted the data to make the type of item (egg, or chicken meat) show in one column rather than have each one in their own columns. This makes it much easier to analyse the summary statistics.
# A tibble: 1,080 × 5
month year Remove `eggType/cknType` avgPrice
<chr> <chr> <lgl> <chr> <dbl>
1 Jan 2004 NA XL_Dozen 230
2 Jan 2004 NA XL_1/2_Doz. 132
3 Jan 2004 NA L_Dozen 230
4 Jan 2004 NA L_1/2_Doz 126
5 Jan 2004 NA Ckn_Whole 198.
6 Jan 2004 NA Ckn_BS_Breast 646.
7 Jan 2004 NA Ckn_Bone_Breast 0
8 Jan 2004 NA Ckn_Whole_legs 194.
9 Jan 2004 NA Ckn_Thighs 0
10 February 2004 NA XL_Dozen 230
# … with 1,070 more rowsI have included the summary statistics of price of chicken and eggs each year combined.
# A tibble: 10 × 6
year sd_year max_year min_year avg_year med_year
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2004 162. 646. 0 241. 204.
2 2005 152. 646. 128. 268. 222
3 2006 152. 646. 128. 269. 222
4 2007 151. 646. 128. 270. 222
5 2008 145. 646. 132 283. 237
6 2009 140. 646. 174. 292. 248
7 2010 140. 646. 174. 290. 235
8 2011 139. 638. 174. 288. 235
9 2012 155. 704. 173. 296. 238.
10 2013 157. 704. 178 297. 238.Additionally, I have calculated the summary statistics of each type of item sold. However, there are some limitations of this. There are two items, chicken bone in breast and chicken Thigs that did not have data for some of the years. This threw off the aveage and standard deviations for those year, but the median remains consistent.
# A tibble: 9 × 6
`eggType/cknType` sd_year max_year min_year avg_year med_year
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Ckn_BS_Breast 23.3 704. 638. 655. 646.
2 Ckn_Bone_Breast 85.5 390. 0 371. 390.
3 Ckn_Thighs 20.8 222 0 216. 222
4 Ckn_Whole 12.5 248 198. 231. 235
5 Ckn_Whole_legs 2.01 204. 194. 203. 204.
6 L_1/2_Doz 22.6 178 126 155. 174.
7 L_Dozen 18.5 278. 225 254. 268.
8 XL_1/2_Doz. 24.7 188. 132 164. 186.
9 XL_Dozen 22.8 290 230 267. 286.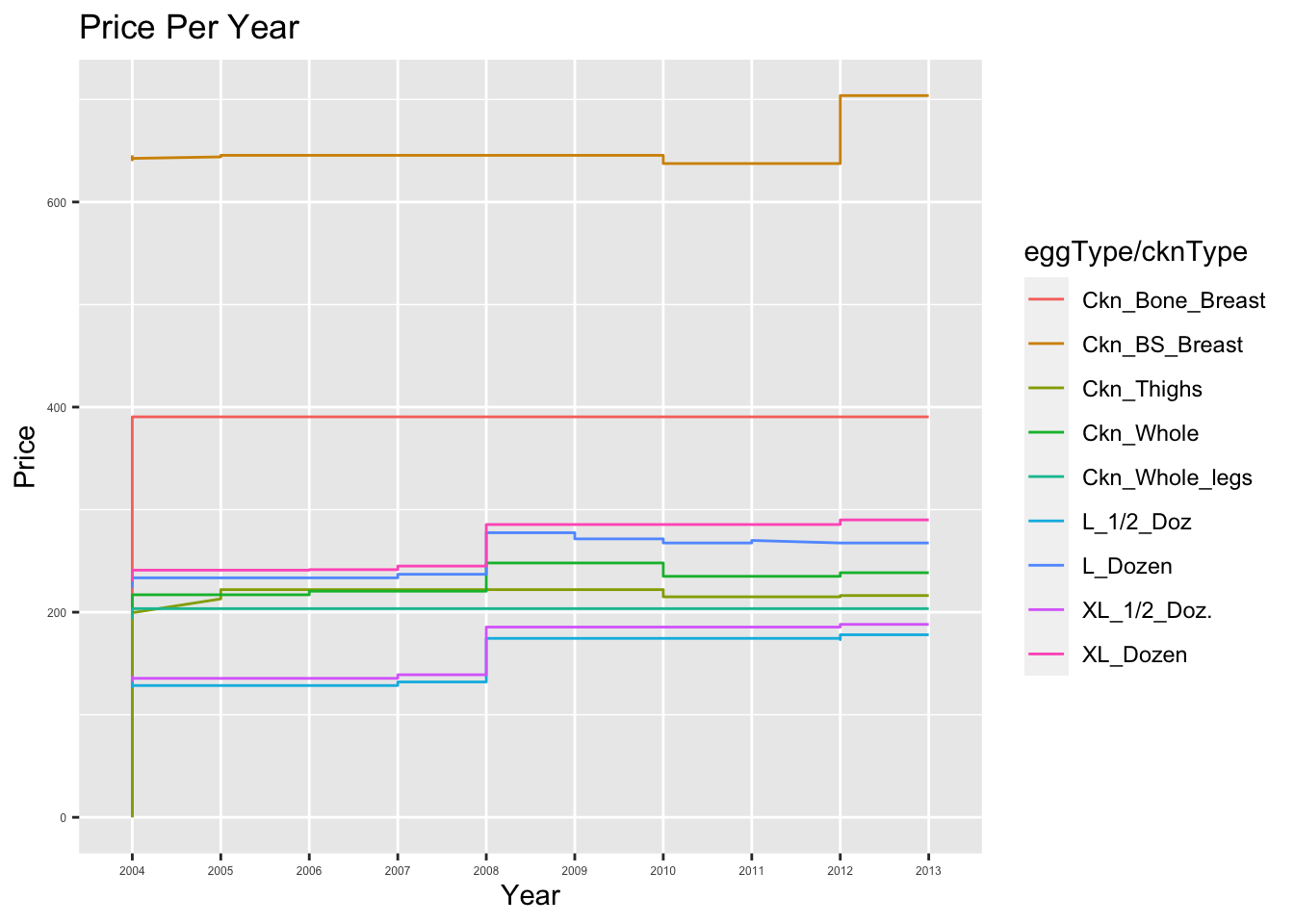
I have included a color coded grab that shows a visual representation of the price per item per year. ## Anticipate the End Result
The pivoted data has 5 rows and 1080 columns.
---
title: "Keith Martin Challenge 3"
author: "Keith Martin"
description: "Tidy Data: Pivoting"
date: "3/17/2023"
format:
html:
toc: true
code-fold: true
code-copy: true
code-tools: true
categories:
- challenge_3
- eggs
---
```{r}
#| label: setup
#| warning: false
#| message: false
library(tidyverse)
library(googlesheets4)
library(readxl)
knitr::opts_chunk$set(echo = TRUE, warning=FALSE, message=FALSE)
```
## Challenge Overview
In this challenge, I decided to use the excel version of the Organice Poultry Data. Before I could read into the data, I needed to include libraries that allowed me to read in excel files.
## Read in data
After reading in the data, I noticed that there we're three different tabs within the excel file. I decided to use only the data tab as this was the first excel file I have read into R.
```{r}
### Loading in the libraries of the excel files
excel_sheets("_data/organiceggpoultry.xls")
```
I decided to re-name the names of the columns so they we're more easily identified. This will become helpful later when I pivot the data longer. Additionally, there is a row that needed to be removed from the data that split the egg prices and the chicken prices. By re-naming the cells it is easier to analyze the data.
```{r}
raw_poulty<-read_excel("_data/organiceggpoultry.xls",
sheet = "Data",
range =cell_limits(c(6,2),c(NA,12)),
col_names = c("date", "XL_Dozen", "XL_1/2_Doz.", "L_Dozen", "L_1/2_Doz", "Remove", "Ckn_Whole", "Ckn_BS_Breast", "Ckn_Bone_Breast", "Ckn_Whole_legs", "Ckn_Thighs"),
)
raw_poulty %>%
select(-c(Remove))
```
```{r}
### Display the months for cleaning purposes
raw_poulty %>%
count(date)
```
```{r}
### remove that /1 from the February date
raw_poulty_clean <-raw_poulty %>%
mutate(date = str_remove(date, " /1"))
### Separate the month and the year, fill the years in for the rest of the months
raw_poulty_clean<-raw_poulty_clean %>%
separate(date, into=c("month", "year"), sep =" ")%>%
fill(year)
raw_poulty_clean
```
This data did not include the year for each month entry. There was also a mistake in the data that needed to be removed.
Additionally, the Chicken Bone Breast and the Chicken Thighs data containted characters rather than numbers. First, I had to change those words to 0. Then, I had to change them to a numerical number, rather than just a character.
```{r}
ckn_edited<- raw_poulty_clean %>%
mutate(Ckn_Bone_Breast = recode(Ckn_Bone_Breast, `too few` = "0"),
Ckn_Thighs = recode(Ckn_Thighs, `too few`="0"))
ckn_edited
```
```{r}
ckn_edited$Ckn_Bone_Breast<-as.numeric(ckn_edited$Ckn_Bone_Breast)
ckn_edited$Ckn_Thighs<-as.numeric(ckn_edited$Ckn_Thighs)
ckn_edited
```
The original clean data had 12 columns and 120 rows.
```{r}
ncol(ckn_edited)
nrow(ckn_edited)
```
### Briefly describe the data
I pivoted the data to make the type of item (egg, or chicken meat) show in one column rather than have each one in their own columns. This makes it much easier to analyse the summary statistics.
```{r}
###pivot the data to longer version for eggs data set
eggs_longer<- pivot_longer(ckn_edited, cols=c("XL_Dozen", "XL_1/2_Doz.", "L_Dozen", "L_1/2_Doz", "Ckn_Whole", "Ckn_BS_Breast", "Ckn_Bone_Breast", "Ckn_Whole_legs", "Ckn_Thighs"),
names_to = "eggType/cknType",
values_to = "avgPrice"
)
eggs_longer
```
I have included the summary statistics of price of chicken and eggs each year combined.
```{r}
eggs_longer%>%
group_by(year)%>%
summarise (
sd_year = sd (avgPrice, na.rm=TRUE),
max_year = max(avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE),
min_year = min(avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE),
avg_year = mean (avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE),
med_year = median(avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE)
)
```
Additionally, I have calculated the summary statistics of each type of item sold. However, there are some limitations of this. There are two items, chicken bone in breast and chicken Thigs that did not have data for some of the years. This threw off the aveage and standard deviations for those year, but the median remains consistent.
```{r}
eggs_longer%>%
group_by(`eggType/cknType`)%>%
summarise (
sd_year = sd (avgPrice, na.rm=TRUE),
max_year = max(avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE),
min_year = min(avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE),
avg_year = mean (avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE),
med_year = median(avgPrice, na.rm = TRUE)
)
```
```{r}
eggs_longer%>%
ggplot(aes(x=year, y=avgPrice, group=`eggType/cknType`, color=`eggType/cknType`)) +
geom_line() +
theme(axis.text=element_text(size=4.5)) +
ggtitle("Price Per Year") +
xlab("Year") + ylab("Price")
```
I have included a color coded grab that shows a visual representation of the price per item per year.
## Anticipate the End Result
```{r}
nrow(eggs_longer)
ncol(eggs_longer)
```
The pivoted data has 5 rows and 1080 columns.